Describe the Three Types of Vesicles.
COPI-coated vesicles Move materials from the ERGIC and golgi. The fluid inside these sacs may be clear white yellow or mixed with blood.
Vesicle Functions Types Of Vesicles 9 Major Functions Of Vesicles
Vacuoles Lysosomes Transport vesicles Secretory vesicles Extracellular vesicles Vacuoles and Vesicles Vacuoles are a type of vesicle that regulates pressure.

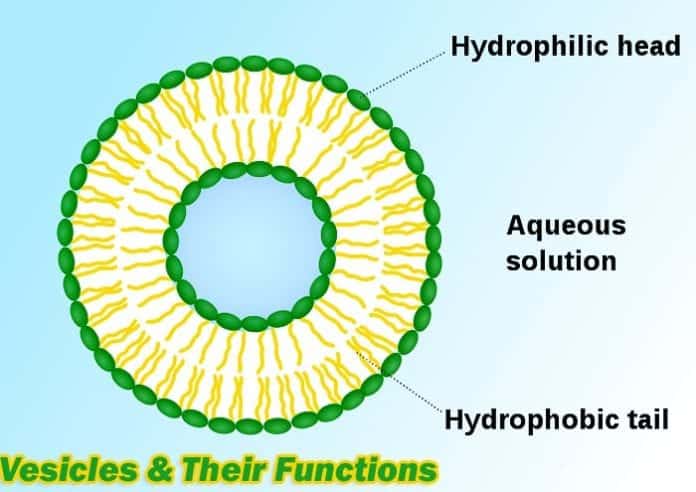
. Vesicles are small fluid-filled sacs or blisters that can appear on your skin. Two other types of coated vesicles have been identified as budding from the ER and Golgi complex. And where would each of the three types be found in the exocytotic and endocytic pathways of the cell.
Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport. Many organisms will use vacuoles as storage areas and some plant cells have very large vacuoles. What is the general purpose of these coat proteins.
Alternative models to describe the endocytosis phase of synaptic vesicle recycling are associated with time scales of vesicle recovery ranging from milliseconds to tens of seconds. Synaptic vesicles are. 3 types of protein coated vesicles.
Transcytosis Vesicular transport within the cell is called transcytosis or cytopempsis. Vesicle fuses with endosome for processing and sorting. Vesicle detaches from membrane.
These is a close-up picture of typical lesions. There are three primary types of endocytosis. Vesicles are fluid-filled lesions less.
Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport. Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that can have secretory excretory and storage functions. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components.
Some of the types of vesicles include. Larger blisters like these are called bullae. It is rather just like exocytosis and endocytosis.
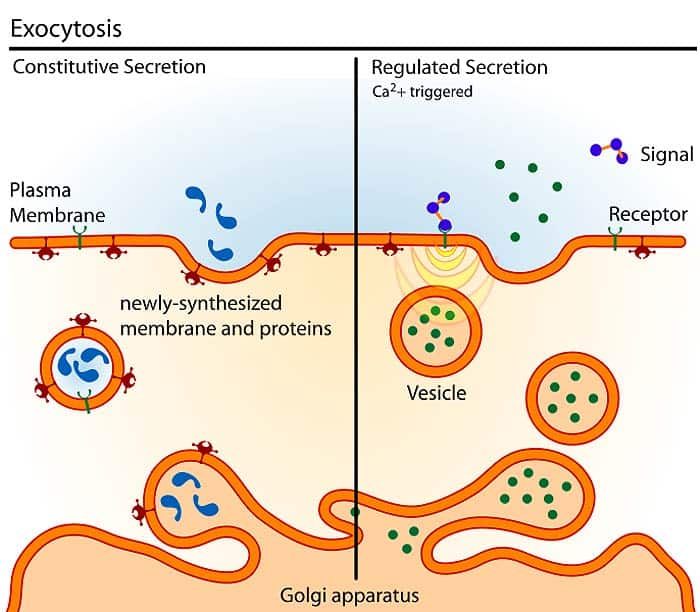
Additionally enzymes within plant vacuoles can. Exocytosis is the process of secreting proteins from a cell into the medium by transport in membranous. These vesicles are called nonclathrin-coated or COP-coated vesicles COP stands for coat protein.
First week only 499. Contractile vacuoles are organelles that undergo periodic growth and contraction in order to. Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system Figure 1.
There have been suggestions that one of the major models envisioned as a slow process that occurs only after complete. Endocytosis is process by which proteins at the surface of the cell are internalized being transported into the cell within membranous vesicles. Clathrin coats are found on vesicles trafficking between the Golgi and plasma membrane.
The vesicle is pinched off from the membrane as the ends of the in-folded membrane fuse together. Enumerate the three types of coat proteins and describe the characteristics of the vesicles that they are associated with. Examples of Vesicles Vacuoles.
There are three main types of coat protein associated with transport vesicles. The vesicle coat selects specific proteins as cargo. Start your trial now.
COPII-coated vesicles Move materials from the ER forward to the ERGIC and golgi complex. Clathrin COPI and COPII. There are three types of vesicle coats.
The various types of coat proteins help with sorting of vesicles to their final destination. I vesicle formation ii vesicle transportation and iii docking in the cell. The hormones that are secreted from the endocrine glands are also stored in secretory vesicles from where they.
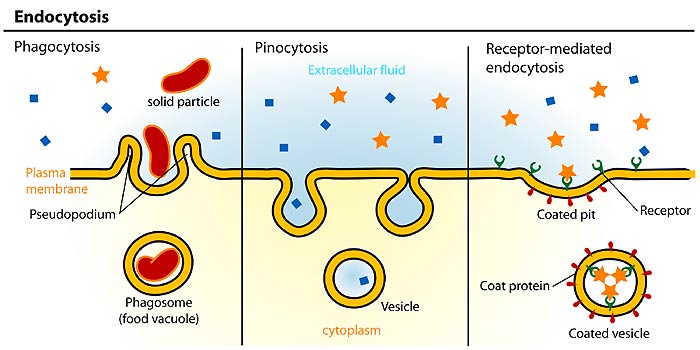
Cells perform three main types of endocytosis. Vacuoles are usually much larger than vesicles. One class of these vesicles COPII-coated vesicles bud from the ER and carry their cargo forward along the secretory pathway to the Golgi apparatus.
Phagocytosis is the process by which cells ingest large particles including other cells by enclosing the particles in an extension of the cell membrane and budding off a new vesicle. 3 fundamental actions associated with this process are. Nearly all plant cells and many protists and fungi have a central fluid-filled compartment called the vacuole.
During pinocytosis cells take in molecules such as water from the extracellular fluid. The internalized vesicle is then processed by the cell. Very small blisters are called vesicles.
In this type of secretory vesicle function of the organelle consists of storing neurotransmitters. Clathrin COPI and COPII. Phagocytosis pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
They are vacuoles lysosomes transport vesicles and secretory vesicles. May recycle back components to the membrane. Material is enclosed by in folding of plasma membrane called a coated pit.
Vacuoles are vesicles that contain mostly water. These complexes cluster in the membrane forming a vesicle buds or coated pit. There are essentially four types of vesicles used by cells.
Describe the mechanisms by which a transport vesicle is able to find and fuse with its target membrane. It selects cargo proteins by binding to sorting signals. Enumerate the three types of coat proteins and describe the characteristics of the vesicles that they are associated with.
Clathrin coats are found on vesicles trafficking between the Golgi and plasma membrane the Golgi and endosomes and the plasma membrane and endosomes. Coated vesicles are vesicles whose membrane has on its surface a layer of a protein such as clathrin cop-I or COP-II. The large central vacuole of the plant cell is used for osmotic control storage of water and nutrient.
A vesicle is a small fluid-filled blister on the skin. There are different types of secretory vesicles like synaptic vesicles which are located at pre-synaptic terminals in the neurons. Pemphigus is classified as one of the blistering diseases.
There are three types of vesicle coats.
Vesicle Functions Types Of Vesicles 9 Major Functions Of Vesicles
Vesicle Functions Types Of Vesicles 9 Major Functions Of Vesicles

Three Types Of Endocytosis Receptor Mediated Pinocytosis And Phagocytosis Plasma Membrane Human Anatomy And Physiology Science Notes

Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis Are Different Mechanisms Of Endocytosis But What Is The Difference Between Them Teaching Biology Biology Classroom Learn Biology
No comments for "Describe the Three Types of Vesicles."
Post a Comment